Paynantheine: Unique Pharmacological Profile
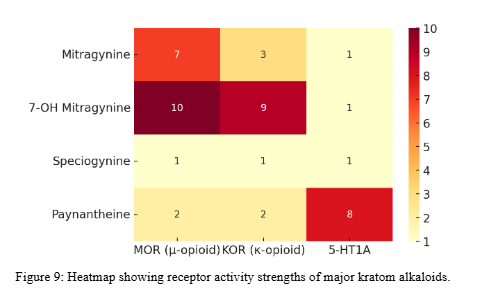
Unlike Mitragynine and 7-Hydroxymitragynine, Paynantheine functions primarily as a competitive antagonist at opioid receptors, offering a modulatory rather than a direct psychoactive effect.
Its pharmacological profile also includes strong 5-HT₁A receptor activity, suggesting potential mood-stabilizing and anxiolytic benefits.
Contribution to Kratom’s Overall Effects
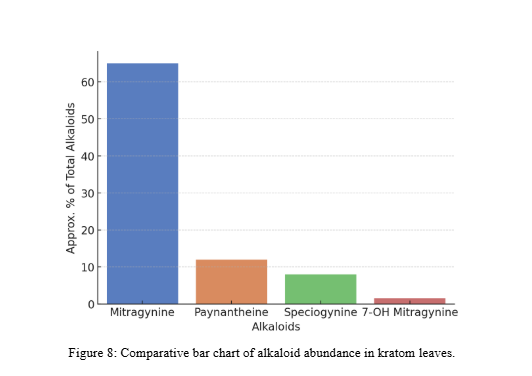
- Despite weaker receptor activity, its relative abundance in kratom ensures it significantly modulates the overall balance of effects.
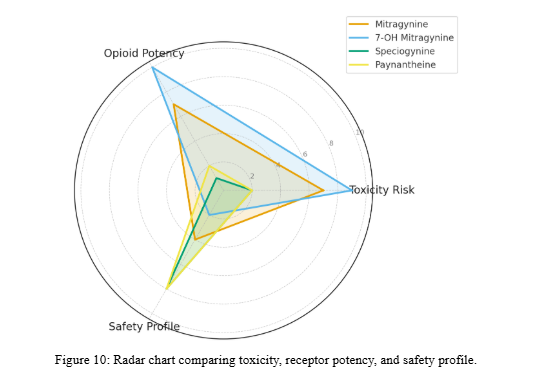
- Acts in concert with Mitragynine and 7-OH Mitragynine to influence kratom’s complex pharmacology.